What is RFID ?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a wireless communications technology used in
applications to identify and receive information about humans, animals
and objects, either in motion or idling.
How work RFID ?
An RFID System consists
of a Reader and a Transponder, which is also called Tag. The data - and
the transmission of energy - take place without any contact through electromagnetic
waves. The transponder is made up of a microchip that is connected to
an antenna. A unique and irreversible identification number is already
determined in the production of the microchip. A passive transponder has
no own energy source and is thereby completely maintenance-free.
The reader (RFID reader)
controls the routine for communication with the transponder through
different function and logic components. An external data interface
transmits the data for the analysis and further processing to an external
computer system (PC).
|
RFID-System:
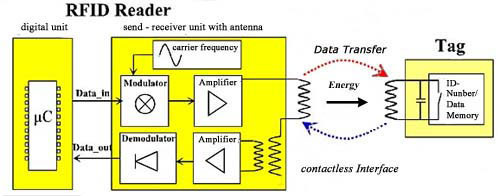
The
microchip and antenna are embedded with the transponder in an encasement,
thus making it insensitive to external influences. The Tags, can
be applied even in an extremely difficult periphery. The transponders
can also be deciphered although covered by a non metallic material or
encasement. The read and write range is dependent on the size of the transponder's
antenna. This can be within a gap of a few centimetres up to over a meter.
Depending on the application, such as smart cards, labels, coins, glass
tubes, etc., the transponder can be custom-built into different forms.
Most of the systems are distinguished with 125 KHz (LF) and 13,56 MHz
(HF).
Application advantages:
- a wide range of areas
of application
- no visible contact
between Tag and Reader
- great diversity in
applications even in harsh enviroments
- forgery proof (unique
ID)
- completely maintenance-free
- faster and safer
data transmission
- combination with
conventional data carriers
Which advantages brings RFID ?
In
comparison to other identification carriers, such as barcodes, the data
can be altered as often as possible through a multi-recordable transponder.
This allow for the information to be available at any time
without connecting to a databank. An anti-collision function (multi-Tag-capable)
permits the recording and separate processing of several Tags in the read-write
phase at one time. A cryptic encoding ensures a secured data exchange
between the reader and the transponder.
RFID - is the optimal technique for:
- stock management
and logistics
- access control, attendance
control
- animal identification
- package and luggage
identification
- industrial automation,
automotive applications
- merchandise control
and labeling
- ref. of origin (product
and trademark protection)
- quality control /
- waste prevention - and dangerous goods logistics
Links
to RFID-Pages:
|
AIM
RFID-Technologies
Industry organisation with Informations on RFID technologies. This
side is sponsored by AIM and is a link to happenings in the RFID
world. |
| |
EUROSMART
EUROSMART is an international non-profit association located in Brussels representing the Voice of the Smart Security Industry for multi-sector applications. |
| |
Global Identification
Global Identification, ID WORLD and ID PEOPLE - the publications of the ID community - are international media that address the global audience of decision makers and key players on both the vendor and on the user side. |
| |
Datamonitor
Datamonitor is a premium business information company helping 5000
of the world’s leading companies across the Automotive, Consumer
Markets, Energy, Financial Services, Healthcare & Technology
sectors. |
| |
|

